Encryption Standards
Germany, France, United Kingdom (UK) & United States (US) encryption standards
What are the Germany, France, United Kingdom (UK) & United States (US) security standards?
We need to determine the sensitivity of the information we are trying to protect. The first reaction would be to use the highest levels of encryption we can, but this might not be the best course of action. Conisder the audience and environment you are working with to determine the key size and overall architecture. What are the requirements for the environment and how much are we willing to spend on such security stances? We will go more in depth in the following pages to help understand what all of this means and how we are going to use these standards to our benefit..
Choosing the Algorithm for the Key and determining the Cipher strength
United States (US) National Security Agency (NSA) Encryption Standards
| Algorithm | Function | Specification | Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) | Symmetric block cipher used for information protection | FIPS Pub 197 | Use 256 bit keys to protect up to TOP SECRET |
| Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman (ECDH) Key Exchange | Pair-Wise Key Establishment Schemes Using Integer Factorization Cryptography | NIST SP 800-56C Rev2 | Use Curve P-384 to protect up to TOP SECRET. |
| Digital Signature Standard (DSS) | Asymmetric algorithm used for digital signatures | FIPS Pub 186-4 | Minimum 3072-bit modulus to protect up to TOP SECRET |
| Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA)-3 | Algorithm used for computing a condensed representation of information | FIPS 202 | SHA3-224, SHA3-256, SHA3-384, and SHA3-512, and two extendable-output functions (XOFs )- SHAKE128 and SHAKE256 |
| Diffie-Hellman (DH) Key Exchange | Semi-Static Key Establishment for TLS 1.3 | IETF-1 IETF-2 RFC7919 | Minimum 4096-bit modulus to protect up to TOP SECRET - Preferred 8192 |
| IP Security (IPsec) | Provide encrypted communication over the Internet | RFC 6071 | Securing Virutal Private Networks (VPN) |
| Secure Hash Standard (SHS) | Hash algorithms that can be used to generate digests of messages | FIPS-180-4 | The digests are used to detect whether messages have been changed since the digests were generated |
| Security Requirements for Cryptographic Modules | Related to the secure design and implementation of a wide range of potential applications and environments | FIPS 140-3 | Mitigation of a plethora of attacks and defines standards |
| RSA | Asymmetric algorithm used for key establishment | NIST SP 800-56C Rev2 | Minimum 3072 bit-modulus to protect up to TOP SECRET. |
| RSA | Asymmetric algorithm used for digital signatures | FIPS 186-4 | Minimum 3072 bit-modulus to protect up to TOP SECRET. |
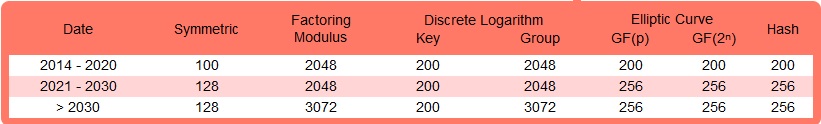
United States (US) National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Encryption Standards
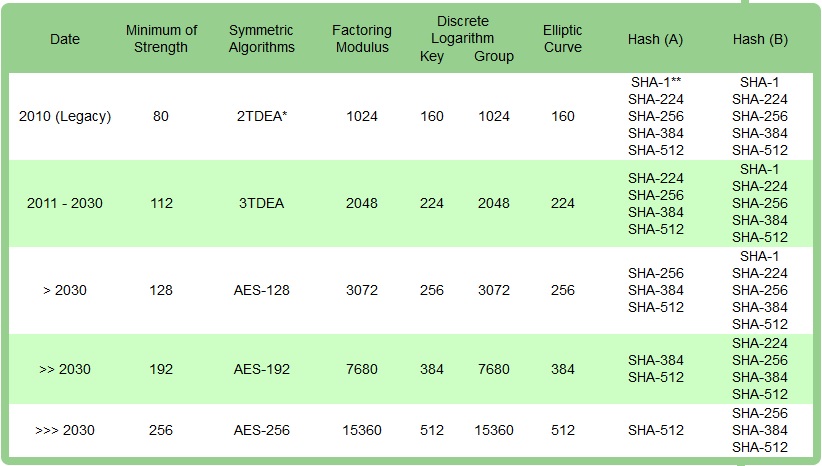
German Government Encryption Standards
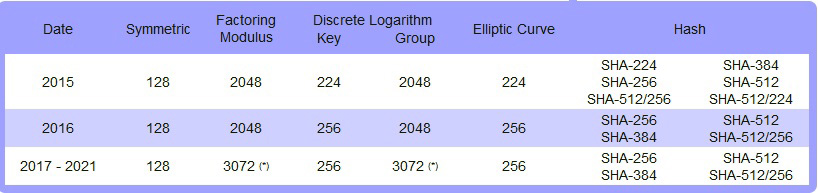
Image by BlueKrypt
French Network and Information Security Agency (ANSSI)