SSO, MFA & PAM Documentation
What is Single Sign-On (SSO)? What are the Benefits and Goals?
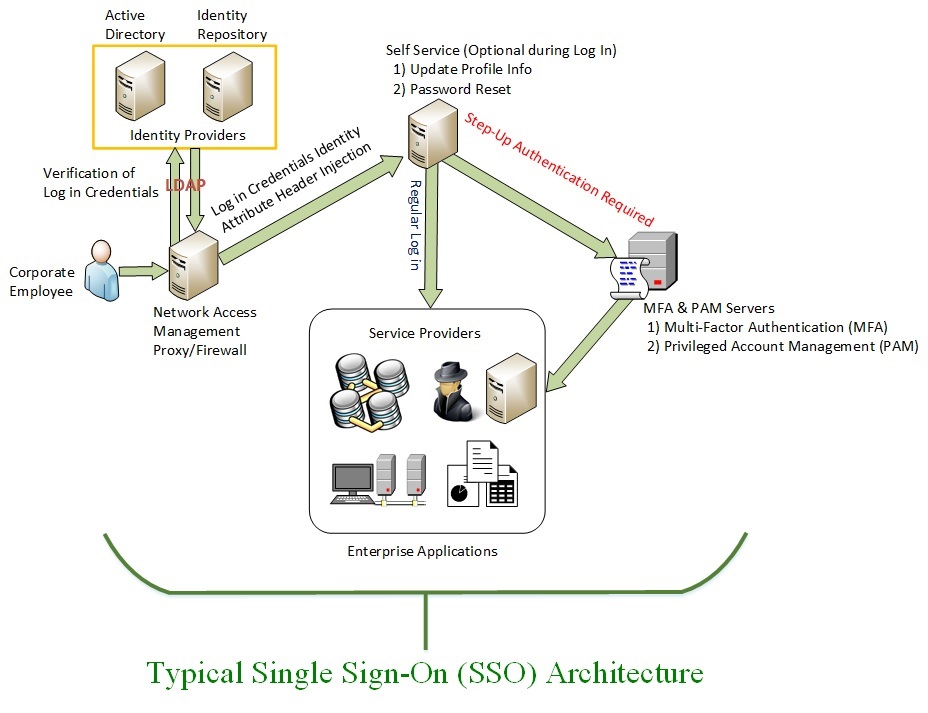
Single Sign-On (SSO)
What is it and what does it do?
Single Sign-On, or SSO, is used for managing seamless account access to desktops, servers, applications, RACF, databases or other systems. SSO is used for setting a security standard(s) for access to enterprise resources. SSO impacts the businesses bottom line by reducing SaaS licensing costs, eliminating redundant processes, and streamlining access to only the required enterprise resources. Provides an audit trail for enterprise resources concerning intellectual property, privacy or compliance with all applicable laws. This may sound like a lot of information to absorb at once, but we will break down each area with basic examples. Then we will combine them into one enterprise architecture to show they work together. The simple architecture is based on three (3) Use Case examples for logging on from internal, external and special situations.
Organizational Benefits
- Lowers the need for users to remember multiple passwords
- Reduces the risk profile to companies
- Reduces helpdesk costs for password resets
- Credential turn on/off easier to manage with role based access
- Higher security standards may be enforced by use of MFA
- Lower the cost for deprovisioning/provisioning
- Integrates with Identity and Access Management
- Allows for workflow's to check for latest credentials and password policies
- Allows for templates and standardization across enterprise access for compliance (PCI, SOX, etc)
- Allows for seamless access with on/off/hybrid premise systems
Goals of Single Sign-On (SSO)
- We want SSO to make end user log in to any authorized application seamless. One secure log in that follows the user around as they alternate between applications.
- Lower the time spent on users not remembering multiple passwords and thus lower help desk password resets costs
- Provide less administration of applications through integration and workflow's
- Allow for secure log in to On/Off premise and Cloud provider resources
- Should be able to use SAML, OAuth, RADIUS, Kerberos or LDAP for secure authentication communications
Accomplished by using secure software for credential authentication and verification between systems